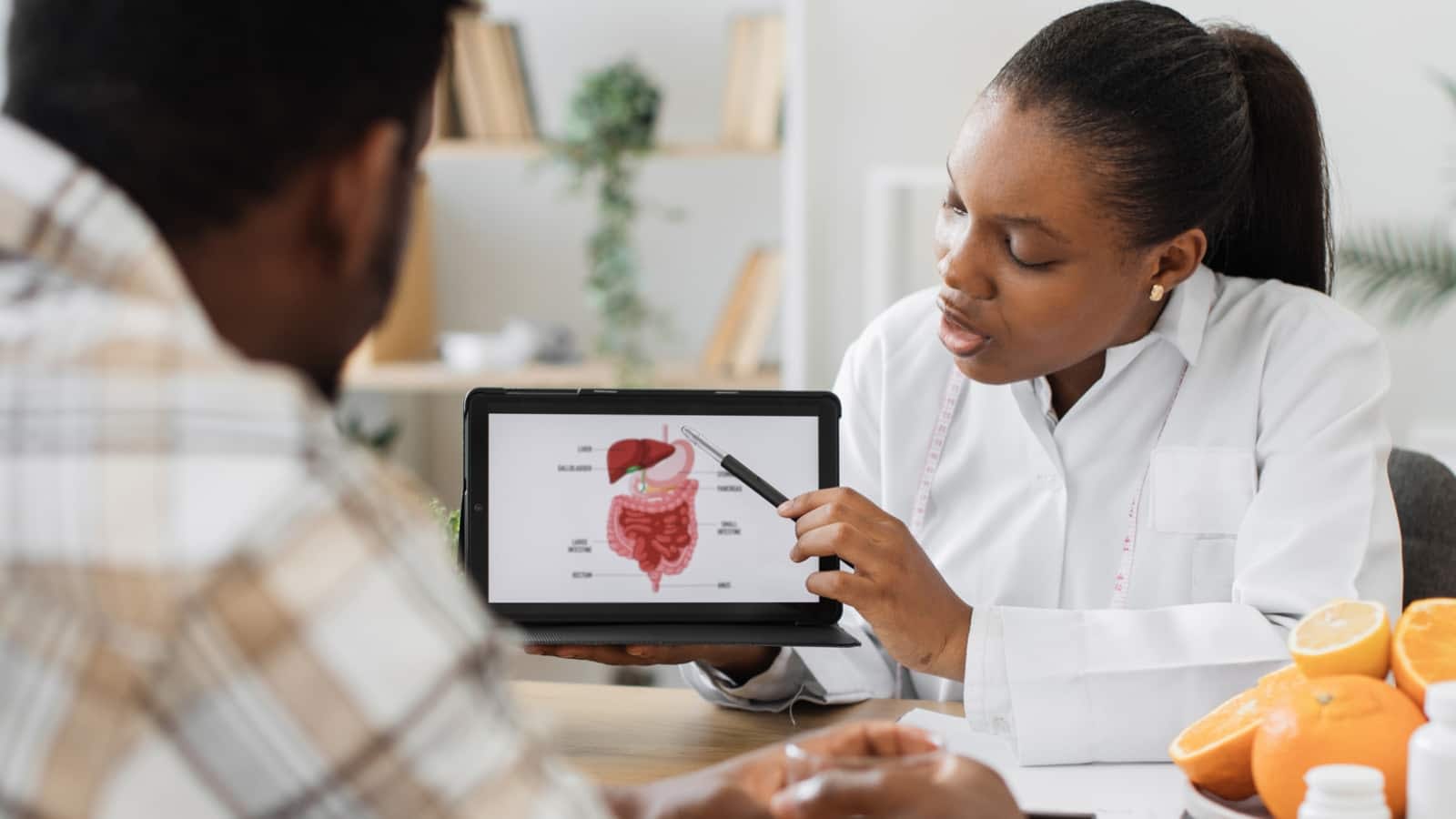
Who knew that a significant part of your health revolves around a microscopic ecosystem inside your gut, influencing everything from digestion to mental health? The gut microbiome is at the core of gut health—a complex community of microorganisms in our digestive tract. Nurturing this intricate ecosystem can improve immunity and nutrient absorption and enhance mental clarity, underscoring the importance of prioritizing gut health daily.
What is the Gut Microbiome?
The gut microbiome refers to the diverse collection of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that inhabit our digestive system. This vast and dynamic community consists of trillions of microbes, each playing a unique role in maintaining our health. The diversity within the gut microbiome is essential, as different microorganisms contribute to various functions such as breaking down complex carbohydrates, synthesizing essential vitamins, and protecting against harmful pathogens. These microorganisms work harmoniously to support critical processes like digestion, nutrient absorption, and regulating our immune system, highlighting their indispensable role in sustaining optimal health.
How the Microbiome Impacts Overall Health
Physical Health:
- Digestion and Nutrient Absorption: The gut microbiome is integral to efficient digestion. It aids in the breakdown of complex foods and facilitates the absorption of vital nutrients. A balanced microbiome ensures our bodies receive the necessary vitamins and minerals to function effectively, promoting energy production and overall vitality.
- Immune System Connection: The gut is home to a major part of the immune system, making the microbiome a crucial player in defending against illnesses. A healthy and diverse microbial population helps prevent chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease by modulating immune responses and reducing inflammation.
Mental Health:
- The Gut-Brain Axis: The gut and brain are in constant communication through the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional network linking the emotional and cognitive centers of the brain with intestinal functions. This connection means that the state of our gut microbiome can significantly influence our mental health and emotional well-being.
- Impact on Mental Health Issues: An imbalanced gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, has been linked to various mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and increased stress levels. The imbalance can disrupt the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are critical for mood regulation.
- Emerging Research: Recent studies suggest that the microbiome may affect cognitive function and mood. Ongoing research explores how specific bacterial strains could potentially be used to enhance mental performance and treat psychiatric disorders. These findings underscore the gut microbiome’s profound influence on our physical and mental health.
Tips for a Healthier Gut
Dietary Changes:
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your diet to provide essential nutrients and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria.
- Fermented Foods: Include foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, which are rich in probiotics that help maintain a balanced microbiome.
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: To support gut health and function, consider supplements or foods that provide probiotics (live beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics (food for these bacteria).
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Stress Reduction: Engage in stress-relieving activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises, as chronic stress can negatively impact gut health.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow your body and gut microbiome to repair and regenerate.
- Regular Physical Activity: Maintain an active lifestyle through regular exercise, which has been shown to promote a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
- Proper Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to aid digestion and support the overall function of the digestive system.
Avoiding Gut Disruptors:
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce your intake of processed and high-sugar foods, which can harm beneficial gut bacteria and promote inflammation.
- Be Cautious with Antibiotics: Use antibiotics only when necessary, as they can disrupt the gut microbiome’s balance by killing harmful and beneficial bacteria.
- Avoid Artificial Sweeteners: Artificial sweeteners have been linked to negative alterations in gut bacteria and metabolic issues.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you experience persistent digestive problems, unexplained fatigue, or noticeable mood changes may indicate underlying gut health issues. Consult with healthcare providers or gastroenterologists for personalized advice and appropriate interventions. Professionals can recommend specific dietary adjustments, prescribe probiotics, or conduct further testing to effectively address and manage gut-related concerns.
Boost Your Well-Being Today
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall health and well-being. By making mindful dietary and lifestyle choices, you can support your gut microbiome and enjoy improved physical and mental health. Start implementing small, sustainable changes today to pave the way for a healthier, happier you. Granted, navigating the healthcare system can be a gut-wrenching experience for anyone. Call your local agent today for assistance in exploring an effective health insurance solution for your problems.